




Data science, analytics, big data, machine learning, and other contemporary applications are being used more frequently as a result of a rising trend among businesses looking for current solutions to handle their business problems.
Data science, analytics, big data, machine learning, and other contemporary applications are being used more frequently as a result of a rising trend among businesses looking for current solutions to handle their business problems.
The amount of unorganised data is growing by the day in our digital age. Many possibilities have opened up in the Big Data world thanks to this enormous amount of data.
Data analytics and data science are included in this. Although these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they all serve different but equally important functions, and there are fundamental differences between these ideas.
In this blog we will be discussing the differences between data science, data analytics, and big data.
Facts and other pieces of information are collected as data. Data is either structured or unstructured in the real world. Let’s first comprehend the different types of data .
Structured data: This type of Data has a defined structure and an order. It is simple to store and access structured data since it is reliable and clearly defined. Also, since we can utilise indexes to store structured data, data searching is simple.
Unstructured data: It is an irregular type since it lacks any logical organisation, structure, or sequencing. When we index the unstructured data, it is prone to errors.
Importance Of Data
Organisations can use data to improve the quality of their work, gain insightful knowledge, forecast trends, avoid hazards, save time, increase profitability, and help them make better decisions.
Look at the statistics below to see what happens in the daily data life:
Average daily: People across the world:
Data is one of the biggest assets any company has in the present time.
Despite the fact that there are significant differences between the ideas of big data, data science, and data analytics, people sometimes use them interchangeably.
As a result, candidates frequently choose in error a job role that does not fit their skills. Hence, understanding how they differ from one another is crucial.
Big Data comprises tools and procedures that collect data, consistently store it, and then extract information that is useful from the data.
Massive amounts of information are referred to as “big data.” It deals with very huge and complex data sets that are beyond the capabilities of a conventional data processing system.
Big data is a concept that combines the three Vs of variety, volume, and velocity, according to experts. Big data is simply more sophisticated, extensive, and large-scale data.
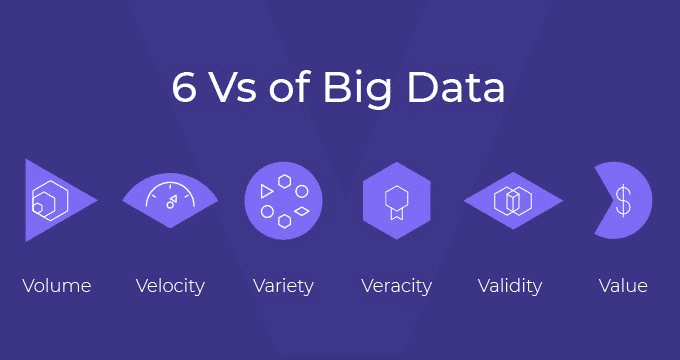

There are certain characteristics of Big Data that define its structure and importance.
Volume: A substantial volume of data is generated every day from numerous sources. Storing this big data used to be a superfluous task. However we can store these massive amounts of information efficiently with the aid of Big Data Hadoop.
Variety: It is used to understand data trends and satisfy market wants. Many data have been gathered from various sources. It could be unstructured text, an image, a document, a video, or an audio file. Processing this range of organised and unstructured data is made easier by the technologies of big data.
Velocity: Velocity describes how quickly this data is being generated and processed. The number of Internet users is rising quickly in this digital age.
Veracity: It has to do with the quality of the information gathered. In order for the data that is collected by organisations to be useful to them, the quality of the data must be carefully considered.
Value: Big Data concentrates on gathering information that has some commercial value for the enterprises. This increases their ability to compete in the market and boosts their earnings.
Variability: Market trends are constantly changing. Variability is the frequency of this shift. Big Data assists in managing these data drifts that enable businesses to develop the newest items.
Data analytics aims to offer relevant insight into difficult business situations. A data analyst’s main interest is analysing historical data from a modern angle and then coming up with novel and difficult business scenarios. Then he or she employs procedures to identify superior solutions. In addition to this, a data analyst forecasts future opportunities that the business can take advantage of.
Data analysts gather information from various sources for their organisations. In order to visualise the data, they do exploratory data analysis. They next check the reports produced with the use of the Data Analytics tools, filtering and cleaning the data as necessary. After that, a data visualisation tool is used to analyse the data. Also, they provide efficient techniques to enhance data statistical analysis. Organisations can use this to record market trends or growth.
The following are a few of the tools for data analytics:
Python, R, Tableau, SAS, RapidMiner, KNIME, QlikView, and Splunk
It employs methods to extract interesting patterns and trends from the data. Data scientists are in charge of finding the facts buried in the interconnected web of unstructured data. Making crucial company decisions in line with current market trends is made easier thanks to this. Machine learning models are built on top of the displayed data as part of data science.
Understanding business requirements: Data scientists do a structural examination of the business model to comprehend business requirements. They then comprehend consumer demands and market trends. This assists in identifying company requirements.
Collecting data: gathering data Data science requires the gathering of useful data as a vital first step. The information is gathered from many sources.
Data comprehension: Understanding the data comes after data collecting. Data scientists employ tools and approaches for data visualisation for this.
Preparation of data: Data Scientists prepare data in line with the needs of companies, which must base strategies and models on data. Let’s say that data scientists are required to prepare the information pertinent to the current fashion trends in order to develop a recommendation system on fashion trends.
Model construction: On top of the generated dataset, data scientists frequently employ machine learning to create systems and models. To create models, data scientists utilise machine learning techniques and algorithms. These models are used by organisations to meet their business needs.
Evaluation of models: Just creating a model is insufficient. They must evaluate the model’s correctness. They therefore train and assess the developed model using various sets of data.
Application of the model: The model is deployed for implementation after being tested for performance.
Process iteration: Machine learning-based systems gain knowledge from their experiences. Data scientists expose them to a range of real-time datasets for this purpose. Also, the models get more precise through the iterative learning process.
Data scientist’s tools
Data scientists utilise the following tools to carry out the aforementioned steps:
Probability and statistics
Programming in R and Python, using Tableau and Power BI to visualise data, and using machine learning techniques.
Interested in learning Data Analytics ? Click here to learn more about these courses Data analytics and Data science
© 2023 Torilo Academy. All right reserved
© 2021 Torilo Academy. All right reserved